Sum Root to Leaf Numbers
You are given the root of a binary tree containing digits from 0 to 9 only.
Each root-to-leaf path in the tree represents a number.
- For example, the root-to-leaf path
1 -> 2 -> 3represents the number123.
Return the total sum of all root-to-leaf numbers. Test cases are generated so that the answer will fit in a 32-bit integer.
A leaf node is a node with no children.
Example 1:
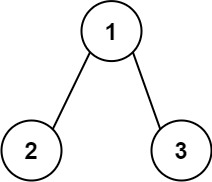
Input: root = [1,2,3]
Output: 25
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 1->2 represents the number 12. The root-to-leaf path 1->3 represents the number 13. Therefore, sum = 12 + 13 = 25.Example 2:
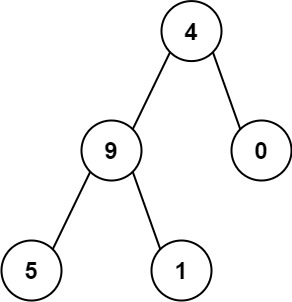
Input: root = [4,9,0,5,1]
Output: 1026
Explanation:
The root-to-leaf path 4->9->5 represents the number 495. The root-to-leaf path 4->9->1 represents the number 491. The root-to-leaf path 4->0 represents the number 40. Therefore, sum = 495 + 491 + 40 = 1026.
Constraints:
- The number of nodes in the tree is in the range
[1, 1000]. 0 <= Node.val <= 9- The depth of the tree will not exceed
10.
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def __init__(self) :
self.result = 0
def sumNumbers(self, root: Optional[TreeNode]) -> int:
self.dfs(root, 0)
return self.result
def dfs(self, root: Optional[TreeNode], curr_val: int) -> int :
nxt = curr_val * 10 + root.val
if root.left : # left가 존재하면
self.dfs(root.left, nxt)
if root.right : # right가 존재하면
self.dfs(root.right, nxt)
if root.left is None and root.right is None: # 둘 다 존재하지 않는다면
self.result += nxt
return이런 식으로 클래스를 하나 구현하는 문제는 아직도 익숙해지지 않는다. 빨리 익숙해져야 할텐데.
__init__ 함수에 반환할 result 를 선언하고, 결과값을 반환할 sumNumbers 함수에 dfs 초기값인 root, 0 을 넣어 준 후 result 값을 반환한다.
dfs는 다음 값인 nxt에 현재값을 * 10 을 하고 현재 노드인 root.val 을 추가한다. 만약 현재 노드에서 왼쪽에 리프 노드가 존재하면 dfs를 재귀하여 진행하고, 오른쪽 리프 노드 역시 마찬가지로 진행한다. 만약 두 노드가 다 존재하지 않으면, 이 값은 최종 값이므로 result에 추가한 후 반환한다.
여기서 not root.left를 사용할까 말까 하다가 하지 않았다. 여기서는 left: 0 이런식으로 표현이 되게 되면 left에는 값이 있는 것으로 되겠지만, 실제로 값이 없는 상황이라면 None으로 표시될 것이다.
TreeNode{val: 4, left: TreeNode{val: 9, left: TreeNode{val: 5, left: None, right: None}, right: TreeNode{val: 1, left: None, right: None}},
right: TreeNode{val: 0, left: None, right: None}}실제 값은 이러하다. 그렇기 때문에 0 도 값이 있는 것으로 되어 답이 정상적으로 출력된 것이다. 근데 파이썬에서 0은 False를 의미하기도 하기 때문에 not root.left 이런식으로 썼다가 Fail이 날까봐 쓰지 않았다.
이것에 대해서도 생각해볼 필요가 있을 듯 하다.
'알고리즘 스터디' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Leetcode/파이썬] 61. Rotate List (0) | 2025.10.30 |
|---|---|
| [Leetcode/파이썬] 290. Word Pattern (0) | 2025.10.26 |
| [Leetcode/파이썬] 48. Rotate Image (0) | 2025.10.25 |
| [Leetcode/파이썬] 20. Valid Parentheses (0) | 2025.10.19 |
| [Leetcode/파이썬] 86. Partition List (0) | 2025.10.19 |
